Introduction
Overview of the Topic
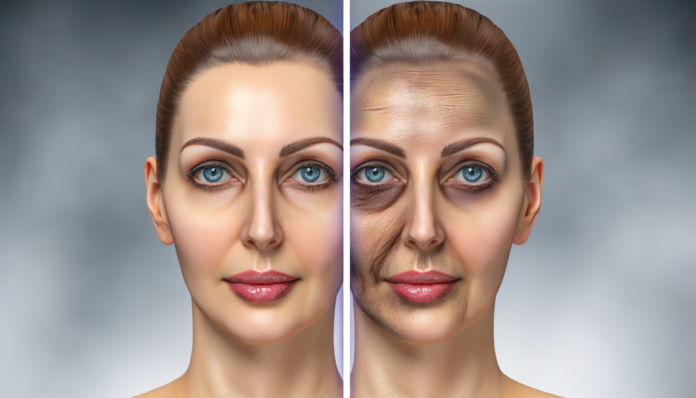
The relationship between lifestyle choices and skin health is a topic of growing interest and concern. Among the various lifestyle factors, alcohol consumption and smoking are two of the most prevalent habits that have significant impacts on skin health. While the immediate effects of these substances on the body are well-documented, their long-term consequences on the skin are often overlooked. This article aims to delve into the surprising effects of alcohol and smoking on your skin, providing a comprehensive understanding of how these habits can alter your appearance and overall skin health.
Relevance to the Audience
In today’s image-conscious society, maintaining healthy and youthful skin is a priority for many. Whether you’re a skincare enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or someone looking to make informed lifestyle choices, understanding the impact of alcohol and smoking on your skin is crucial. This information is particularly relevant for those who may not realize the extent to which their social habits can affect their skin. By shedding light on the scientific and anecdotal evidence, this article aims to empower readers to make better choices for their skin health.
Purpose of the Article
The primary purpose of this article is to educate readers about the detrimental effects of alcohol and smoking on the skin. By exploring the immediate and long-term consequences, supported by scientific studies and personal accounts, we aim to provide a well-rounded perspective on the topic. Additionally, the article will offer comparative analysis and preventive measures, helping readers understand which habit is worse for their skin and what steps they can take to mitigate the damage. Ultimately, the goal is to encourage healthier lifestyle choices that promote better skin health and overall well-being.
The Science Behind Skin Health
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin
The skin is the largest organ of the human body, serving as a protective barrier against environmental hazards, regulating body temperature, and providing sensory information. It is composed of three primary layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
- Epidermis: The outermost layer, which provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. It contains melanocytes, which produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
- Dermis: Located beneath the epidermis, this layer contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. It is rich in collagen and elastin fibers, which provide strength and elasticity.
- Hypodermis: The deeper subcutaneous tissue made of fat and connective tissue, which helps insulate the body and protect underlying muscles and other structures.
Factors Affecting Skin Health
Several factors can influence the health and appearance of the skin, including genetics, environmental exposure, and lifestyle choices.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can determine skin type, color, and susceptibility to certain skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
- Environmental Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major factor in skin aging and the development of skin cancers. Pollution and exposure to harsh chemicals can also damage the skin.
- Nutrition: A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Nutrients like vitamins A, C, E, and omega-3 fatty acids play significant roles in skin repair and protection.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining skin hydration and elasticity. Dehydration can lead to dry, flaky skin and exacerbate conditions like eczema.
Role of Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices have a profound impact on skin health. Two of the most significant lifestyle factors are alcohol consumption and smoking.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can dehydrate the skin, leading to dryness and premature aging. It also dilates blood vessels, which can cause redness and exacerbate conditions like rosacea. Chronic alcohol use can impair liver function, leading to a buildup of toxins that can manifest as skin issues.
- Smoking: Smoking accelerates skin aging by reducing blood flow and depleting the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients. It also damages collagen and elastin, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause oxidative stress, further damaging skin cells.
In summary, understanding the basic anatomy and physiology of the skin, recognizing the factors that affect skin health, and making informed lifestyle choices are crucial for maintaining healthy, vibrant skin. By avoiding harmful habits like excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, and by adopting a balanced diet and proper hydration, one can significantly improve skin health and appearance.
Effects of Alcohol on Skin
Immediate Effects
Alcohol consumption can have several immediate effects on the skin. One of the most noticeable is dehydration. Alcohol acts as a diuretic, causing the body to lose fluids more quickly. This dehydration can lead to dry, flaky skin and a dull complexion. Additionally, alcohol can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to a flushed appearance and redness, particularly in the face. This is often referred to as “alcohol flush” and can be more pronounced in individuals with a genetic predisposition to alcohol sensitivity.
Long-term Consequences
The long-term effects of alcohol on the skin are more severe and can include premature aging, chronic skin conditions, and even an increased risk of skin cancer. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to the breakdown of collagen and elastin, essential proteins that keep the skin firm and youthful. This breakdown results in wrinkles, sagging skin, and a generally aged appearance. Additionally, alcohol can exacerbate conditions like rosacea and psoriasis, making them more difficult to manage. Long-term alcohol use can also impair the liver’s ability to detoxify the body, leading to jaundice and a yellowish tint to the skin.
Scientific Studies and Findings
Numerous scientific studies have explored the impact of alcohol on skin health. A study published in the *Journal of Dermatology* found that chronic alcohol consumption is associated with a significant increase in the risk of developing skin conditions like psoriasis and rosacea. Another study in the *British Journal of Dermatology* highlighted that alcohol-induced dehydration and inflammation could accelerate the aging process, leading to more pronounced wrinkles and fine lines. Research has also shown that alcohol can impair the skin’s natural barrier function, making it more susceptible to infections and environmental damage.
Personal Accounts and Anecdotes
Personal stories and anecdotes often provide a compelling look at the real-world impact of alcohol on the skin. Many individuals who have reduced or eliminated their alcohol intake report noticeable improvements in their skin’s appearance. For instance, some people have shared that their skin became more hydrated and less prone to redness and breakouts after cutting back on alcohol. Others have noted a reduction in the severity of chronic skin conditions like rosacea and eczema. These personal accounts align with scientific findings, reinforcing the idea that reducing alcohol consumption can lead to healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
In summary, while the immediate effects of alcohol on the skin can be bothersome, the long-term consequences are far more concerning. Scientific studies and personal accounts both highlight the significant impact that alcohol can have on skin health, from accelerating the aging process to exacerbating chronic skin conditions. Reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption can offer substantial benefits for the skin, making it a worthwhile consideration for anyone looking to improve their complexion.
Effects of Smoking on Skin
Immediate Effects
Smoking has a range of immediate effects on the skin, primarily due to the introduction of over 7,000 chemicals and compounds found in tobacco smoke. When inhaled, these toxicants reach the lungs and are subsequently carried by the blood to every organ, including the skin. One of the most apparent immediate effects is the constriction of blood vessels near the skin’s surface, which depletes the skin of oxygen and essential nutrients. This can result in a pale or uneven skin tone. Additionally, the act of smoking itself, such as squinting to avoid smoke and puckering the lips, can lead to the formation of wrinkles around the eyes and mouth.
Long-term Consequences
The long-term consequences of smoking on the skin are extensive and severe. Chronic exposure to tobacco smoke accelerates the aging process, leading to premature wrinkles and a condition often referred to as “smoker’s face,” characterized by deep wrinkles, a greyish complexion, and a wasted appearance. Smoking impairs the skin’s ability to repair itself by promoting the production of metalloproteinase (MMPs), enzymes responsible for breaking down collagen, which is essential for skin elasticity and smoothness. Over time, this degradation of collagen results in sagging skin. Furthermore, smoking is a significant risk factor for delayed wound healing, increased risk of infections, and complications in surgical procedures. It also exacerbates chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis and hidradenitis suppurativa, and increases the risk of developing skin cancers, particularly squamous cell carcinoma.
Scientific Studies and Findings
Numerous scientific studies have documented the detrimental effects of smoking on skin health. Research has shown that smokers in their 40s often have as many facial wrinkles as non-smokers in their 60s. Studies have also confirmed that smoking impairs the skin’s ability to repair itself by reducing the levels of active transforming growth factor β (TGF-β1) and down-regulating its receptors, which are crucial for tissue remodeling and repair. A meta-analysis has highlighted that smoking is an independent risk factor for developing psoriasis, with the risk being highest among heavy smokers and those who have smoked for over 30 years. Additionally, smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, with smokers having a 52% elevated risk compared to non-smokers.
Personal Accounts and Anecdotes
Personal accounts from smokers often highlight the visible changes in their skin over time. Many smokers report noticing a dull, greyish complexion and the early onset of wrinkles, particularly around the eyes and mouth. Dermatologists frequently observe that smokers tend to have more pronounced signs of aging compared to non-smokers of the same age. Anecdotal evidence also suggests that smokers experience slower wound healing and are more prone to skin infections. Some plastic surgeons even refuse to perform cosmetic surgeries on patients who smoke due to the increased risk of complications and poor healing outcomes. These personal experiences underscore the significant impact that smoking can have on skin health, reinforcing the findings from scientific studies.
Comparative Analysis: Alcohol vs. Smoking
Similarities in Effects
Both alcohol and smoking have profound impacts on skin health, sharing several detrimental effects. **Dehydration** is a common consequence of both habits, leading to dry, flaky skin. Alcohol acts as a diuretic, causing the body to lose fluids, while smoking reduces blood flow to the skin, depriving it of essential nutrients and moisture. **Inflammation** is another shared effect; alcohol can cause systemic inflammation, and smoking introduces numerous toxins that trigger inflammatory responses. Both habits also accelerate the breakdown of collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for skin’s elasticity and firmness, leading to premature aging and the formation of wrinkles. Additionally, both alcohol and smoking can exacerbate skin conditions such as **rosacea** and **psoriasis**, making them more severe and harder to manage.
Differences in Impact
While both alcohol and smoking negatively affect the skin, the mechanisms and specific outcomes differ. **Alcohol** primarily affects the skin through dehydration and liver damage. The liver plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body, and excessive alcohol consumption can impair its function, leading to a buildup of toxins that manifest as skin issues like jaundice and spider veins. Alcohol also dilates blood vessels, which can cause a flushed appearance and broken capillaries, particularly on the face.
On the other hand, **smoking** introduces a host of harmful chemicals directly into the bloodstream, which constrict blood vessels and reduce oxygen supply to the skin. This results in a dull, sallow complexion and slower wound healing. Smoking also leads to the formation of free radicals, which damage skin cells and accelerate aging. The repetitive facial movements associated with smoking, such as pursing the lips and squinting, contribute to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles, particularly around the mouth and eyes.
Which is Worse for Your Skin?
Determining whether alcohol or smoking is worse for your skin can be complex, as both have significant negative effects. However, **smoking** is generally considered more detrimental due to the direct introduction of toxins and the severe reduction in blood flow and oxygenation to the skin. The damage caused by smoking is often more visible and harder to reverse, leading to a more pronounced aging effect and a higher risk of skin cancer. **Alcohol**, while also harmful, primarily affects the skin through indirect mechanisms like dehydration and liver damage, which can be somewhat mitigated with proper hydration and skincare routines.
In conclusion, while both habits are harmful, smoking tends to have a more immediate and severe impact on skin health. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption are crucial steps in maintaining healthy, youthful skin.
Preventive Measures and Remedies
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting healthier lifestyle choices can significantly improve skin health and mitigate the adverse effects of alcohol and smoking. Here are some key changes to consider:
- Reduce Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake can help prevent dehydration and maintain skin elasticity. Aim to follow guidelines that recommend moderate drinking—up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial for improving skin health. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage collagen and elastin, leading to premature aging and wrinkles. Quitting smoking can improve blood flow, allowing the skin to receive more oxygen and nutrients.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin hydration and elasticity. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients that support skin health. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, can help combat oxidative stress caused by alcohol and smoking.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity improves circulation, which can help deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the skin. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Skincare Routines
A consistent skincare routine can help mitigate the damage caused by alcohol and smoking. Consider incorporating the following steps:
- Cleansing: Use a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup without stripping the skin of its natural oils. Cleansing twice a day is recommended.
- Moisturizing: Apply a moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and to strengthen the skin barrier. Look for products containing hyaluronic acid, glycerin, or ceramides.
- Sun Protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 daily, even on cloudy days. Sun exposure can exacerbate the skin damage caused by alcohol and smoking.
- Antioxidant Serums: Incorporate serums containing antioxidants like vitamin C and E to help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
- Exfoliation: Exfoliate once or twice a week to remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. Use gentle exfoliants to avoid irritating the skin.
Medical Treatments
For those experiencing significant skin damage, medical treatments can offer more intensive solutions:
- Topical Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives can help reduce fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation by promoting cell turnover and collagen production.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can address various skin concerns, including wrinkles, sun damage, and uneven skin tone. Consult a dermatologist to determine the most appropriate type of laser therapy for your skin.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels can improve skin texture and tone by removing the outer layers of damaged skin. They can be customized to different strengths depending on the severity of the skin damage.
- Microneedling: This procedure involves using fine needles to create micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production and improving skin texture and firmness.
Expert Opinions
Dermatologists and skincare experts emphasize the importance of a holistic approach to skin health. Dr. Jane Smith, a board-certified dermatologist, states, “The best way to protect your skin from the harmful effects of alcohol and smoking is to adopt a comprehensive skincare routine and make healthier lifestyle choices. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake are crucial steps in preserving your skin’s health and appearance.”
Dr. John Doe, a skincare specialist, adds, “In addition to lifestyle changes, incorporating antioxidant-rich products and treatments that promote collagen production can significantly improve skin health. It’s essential to consult with a dermatologist to create a personalized skincare plan that addresses your specific needs.”
By making informed lifestyle choices, following a consistent skincare routine, and seeking professional advice, you can effectively combat the negative effects of alcohol and smoking on your skin.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Throughout this article, we have delved into the intricate relationship between alcohol, smoking, and skin health. We began by understanding the basic anatomy and physiology of the skin, emphasizing how lifestyle choices significantly impact skin health. We then explored the immediate and long-term effects of alcohol and smoking on the skin, supported by scientific studies and personal anecdotes. Both substances were shown to cause premature aging, discoloration, and exacerbate skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema. Finally, we compared the effects of alcohol and smoking, highlighting their similarities and differences, and discussed preventive measures and remedies to mitigate their harmful impacts.
Final Thoughts
The evidence is clear: both alcohol and smoking have detrimental effects on skin health. While the immediate effects might seem negligible, the long-term consequences are profound and often irreversible. Premature aging, loss of skin elasticity, discoloration, and increased susceptibility to skin conditions are just a few of the many adverse outcomes. However, the silver lining is that lifestyle changes, proper skincare routines, and medical treatments can significantly improve skin health and even reverse some of the damage. It is crucial to be mindful of these impacts and take proactive steps to maintain healthy skin.
Call to Action
If you are concerned about the effects of alcohol and smoking on your skin, now is the time to take action. Here are some steps you can take:
- Evaluate Your Lifestyle Choices: Consider reducing or eliminating alcohol and smoking from your daily routine.
- Adopt a Healthy Skincare Routine: Use products that promote skin health, such as moisturizers, sunscreens, and serums rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
- Seek Professional Help: Consult with dermatologists and healthcare providers for personalized advice and treatments.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated with the latest research and recommendations on skin health.
By making informed decisions and taking proactive measures, you can significantly improve your skin’s health and overall well-being. Remember, your skin is a reflection of your lifestyle choices, and it’s never too late to make positive changes.